In this beginner’s guide, lets walk through the basic rules to consider when setting up and operating Greenhouses, along with some key rules and tips to ensure your garden thrives.
Part 1: Setting Up Your Greenhouse

Location, Location, Location:
- Find a sunny spot: Look for a location with at least 6 hours of direct sunlight a day.
- Consider wind direction: Protect your greenhouse from strong winds to prevent damage.
Choose Your Greenhouse:
- Start with a simple, affordable structure like a mini-greenhouse or a polyethylene greenhouse.
- Assemble with care: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for set up.
- Remember that a simple cover over a current bed can be a simple version of a greenhouse! Just modify the tips below to fit.
- Options are endless depending on your budget and vision – have some fun searching out the types and styles available.
Prepare the Ground:
- Level the ground: Ensure a stable, level foundation.
- Lay gravel or a weed barrier: Prevent weed growth underneath.
Ventilation and Shading:
- Install vents: Proper ventilation is essential to regulate temperature, humidity, and air quality inside the greenhouse. Without good ventilation, the house can become too hot and stuffy, leading to poor plant growth.
- Roof vents, side vents, louvers (adjustable slats that can open and close
- Fans may be needed depending on size
- Shading: Shading is essential to protect plants from excessive sunlight, especially during the hottest parts of the day. Without adequate shading, the greenhouse can become too hot, leading to sunburned plants and stress.
- Shade cloth, retractable roofs or sides and placement are important to consider
Part 2: Operating Your Greenhouse
Temperature Control:
- Monitor daily temperatures: Keep an eye on the temperature. Remember that specific plant species may have more precise temperature requirements. Always refer to the care instructions for the plants you are growing, and consider using a thermometer to ensure your greenhouse stays within the appropriate temperature range. Additionally, factors like humidity, light levels, and ventilation play a role in the overall health and growth of your plants, so consider these aspects in conjunction with temperature management.
- Use heaters or fans

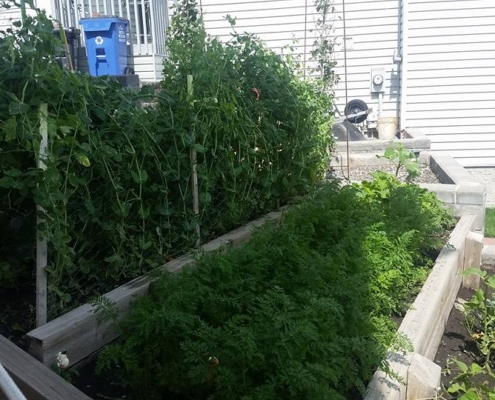
Lesson Learned: The above picture shows some mini greenhouse rows or boxed off plants. The very first time I did something similar in my own garden, I did not realize how they worked, and I completely fried all of my plants underneath the plastic! Learn from my mistakes friends – ventilate and let those babies breath!
Watering and Humidity:
- Water properly: Use a drip irrigation system or hand-water to keep the soil evenly moist. Read your plant instructions to be sure you provide adequate water supply
- Maintain humidity: Spraying the floor with water or using a humidifier can help plants thrive.
Part 3: Rules and Tips for Greenhouse Ownership
Local Regulations:
- Check local zoning laws: Some areas have restrictions on greenhouse size and placement.
- Permits: Determine if you need any permits before building.
Crop Rotation:
- Rotate your crops: Avoid planting the same species in the same spot season after season to keep the soil fertile and healthy. Different plants bring different nutrients to your soil! Also, rotating your plants helps with weed and pest control.
Regular Maintenance:
- Clean and tidy: Other than for safety reasons, we know that cleanliness keeps the germs and pests away.
- Repair damage: Promptly repair any holes, tears, or damage to the greenhouse covering to help the longevity of your structure.

Conclusion:
A home-based greenhouse can elevate your gardening game and provide year-round growing opportunities. By carefully setting up, operating, and adhering to the rules, you can become a successful gardener. Whether you’re growing vegetables, fruits, or flowers, your green thumb adventures. Happy gardening!